6. POLIOMYELITIS
DEFINITION
It is vital infection of human alimentary system. It may be paralysis of brain, spinal cord or nerves.
CAUSATIVE ORGANISM
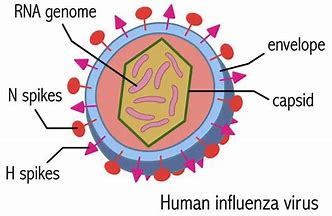
- RNA entero virus
MODE OF TRANSMISSION
- Droplet infection
- Faeco-oral route.
SIGN/SYMPTOMS
They divided into four types:-
1. Aspmpomatic or Subclinical or Silent ImfeInfec: below 90% cases are symptoms.
2. Abortive Police: Virus enter into blood-stream but not effect to nervous system.
3 Non-paralytic Type Polio: 1% in effective Cases. In this type, virus enter into nervous
System but not effect on cells.
The symptoms are :-
- Fever
- Shitffiness of nek
- Backache
- Malaise
- Vomiting
- Headache.
4. Paralytic Polio:-
- Very rare.
- It effect the cell of nervous system.
The Symptoms are:-
- Malaise
- Nausea
- Sore throat
- Anorexia
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Backache
- Stiffness of neck
- Drowsiness
- Irritation
- Tremour
- Flaccid paralysis
TREATMENT
- Ventilatory support
- Strict bed rest
- Sedatives
- Catheterization for retention of urine
- Laxative for constipation.
After recovery corrective surgery is done.
PREVENTION
- Vaccination (two types of vaccination)
1. Sabin
2. Salk.